|
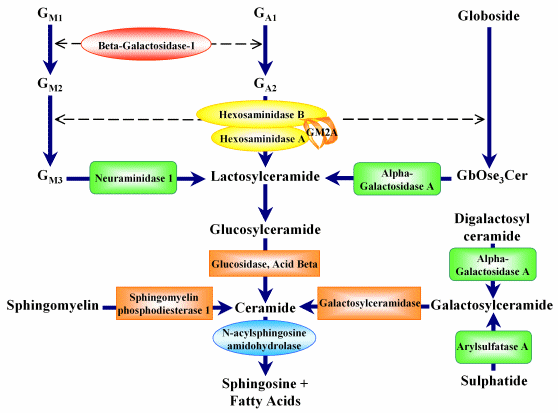
Catabolic Pathway for Glycosphingolipids and Associated Storage Diseases
|
|
|
|
Clinical Disorder |
Gene Symbol |
|---|
|
Gangliosidosis, Generalized GM1, Type I
|
GLB1 |
|
Gangliosidosis, Generalized GM1, Type II
|
GLB1 |
|
Tay-Sachs Disease
|
HEXA |
|
Tay-Sachs Disease AB Variant
|
GM2A |
|
Sandhoff Disease
|
HEXB |
|
Fabry Disease; Angiokeratoma, Diffuse
|
GLA |
|
Gaucher Disease, Type I
|
GBA |
|
Gaucher Disease, Type II
|
GBA |
|
Gaucher Disease, Type III
|
GBA |
|
Niemann-Pick Disease, Type A
|
SMPD1 |
|
Niemann-Pick Disease, Type B
|
SMPD1 |
|
Neuraminidase Deficiency
|
NEU1 |
|
Neuraminidase Deficiency with Beta-Galactosidase Deficiency
|
PPGB |
|
Farber Lipogranulomatosis
|
ASAH1 |
|
Krabbe Disease
|
GALC |
|
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
|
ARSA |
|
|
|
Legend:
The NIGMS Human Genetic Cell Repository has samples which derive from defects in steps in the catabolic pathway encoded by 11 genes as depicted in the diagram shown above. In addition, there are samples from neuraminidase deficiency with beta-galactosidase deficiency, caused by defects in the PPGB gene. By clicking on the symbol for the clinical disorder or enzymatic step in the diagram or the table, the list of the samples and the mutations in these samples appears. By clicking on the Gene Symbol a list of samples with characterized mutations appears.
References:
Jeyakumar et al., Glycosphingolipid lysosomal storage diseases: therapy and pathogenesis. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 28: 343-357 (2002).
Abstract
|
|
|